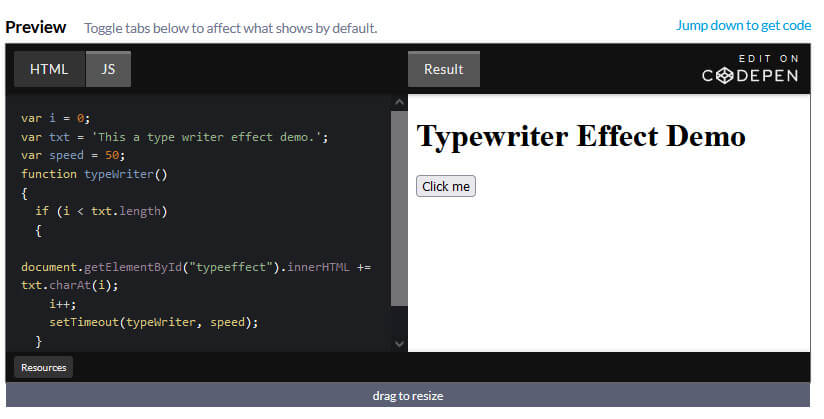
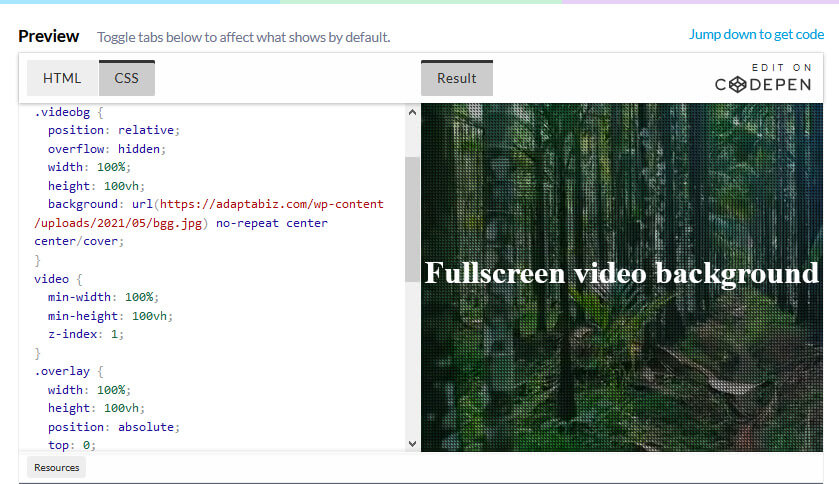
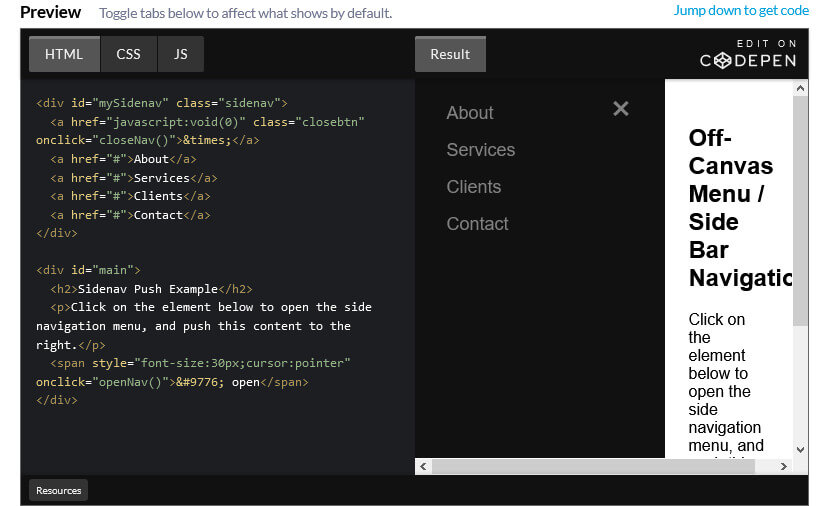
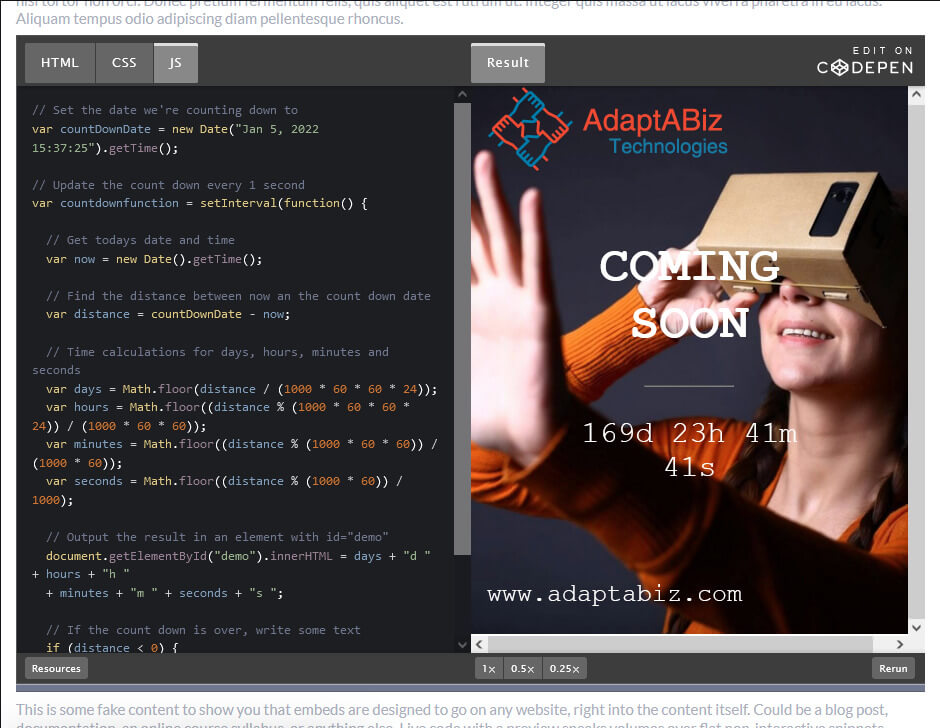
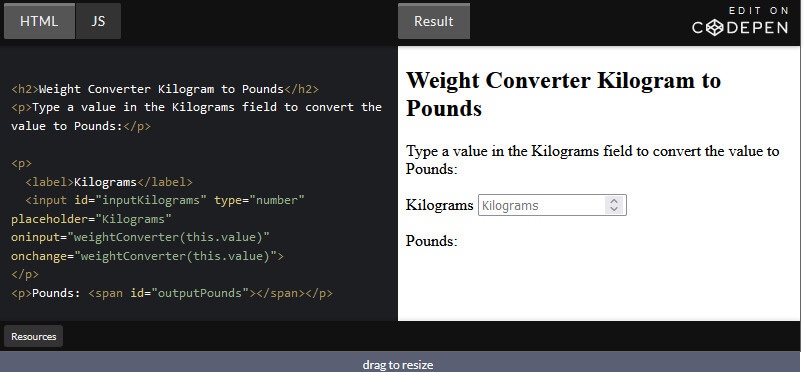
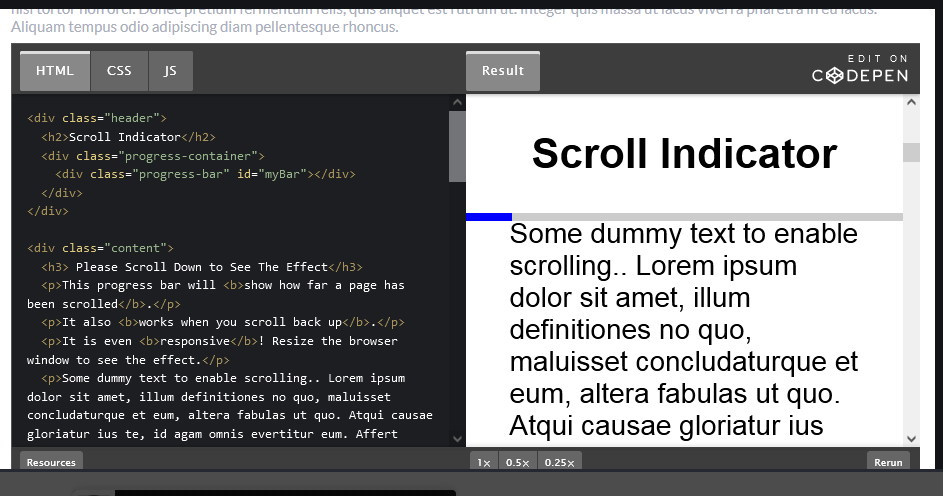
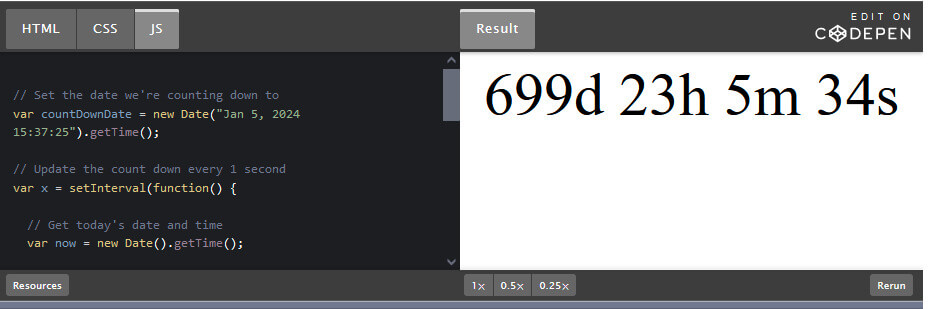
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is a style sheet language that is used to describe the look and formatting of a document written in a markup language.

It provides an additional feature to HTML. It is generally used with HTML to change the style of web pages and user interfaces. It can also be used with any kind of XML documents including plain XML, SVG, and XUL.
While CSS is great for creating text styles, it is helpful for formatting other aspects of Web page layout as well. For example, CSS can be used to define the cell padding of table cells, the style, thickness, and color of a table’s border, and the padding around images or other objects. CSS gives Web developers more exact control over how Web pages will look than HTML does. This is why most Web pages today incorporate cascading style sheets.
Type of Style Sheet
External Style Sheet
The CSS rules in a separate file known as an External style sheet with the help of element. The element is used in web pages to describe the relationship between two documents. The element is always an empty element and when used with style sheets it must carry three attributes.
Advantages of External CSS Style Sheets
- It saves you repeating the same style on each page.
- The appearance of several pages by altering just the style sheet rather than each individual page.
- The style sheet can act as a style template to help the different authors achieve the same style of the document.
CSS Properties
You style HTML elements via CSS properties. Different HTML elements may have different CSS properties you can set. A CSS property declaration consists of a property name and a property value. The property name comes first, then a colon, and then the value. If you specify more than one CSS property, each name-value pair is separated by a semicolon. There are many CSS properties you can specify for different HTML elements.
List of Properties
align-content | It helps to align a flex container’s lines within it when there is extra space in the cross-axis |
align-items | It defines the default behavior for how items are laid out along the cross axis (perpendicular to the main axis). |
align-self | Specifies the alignment for selected items inside a flexible container |
all | Resets all properties |
animation | It can be used to animate many other properties |
animation-delay | Specifies a delay for the start of an animation |
animation-direction | Sets the direction of the animation after the cycle. Its default resets on each cycle |
animation-duration | Specifies the length of time it takes for an animation to complete one cycle |
animation-fill-mode | Sets which values are applied before/after the animation |
animation-iteration-count | Specifies the number of times an animation should be played |
animation-name | Declares the name of the @keyframes animation |
animation-play-state | Specifies if the animation is paused/playing |
animation-timing-function | Specifies the acceleration curve of an animation |
backface-visibility | Defines whether or not the back face of an element should be visible |
background | A shorthand property that allows you to control the background of any element |
background-attachment | Specifies how to move the background relative to the viewport |
background-blend-mode | Defines how an element’s background-image should blend with its background-color |
background-clip | Defines how far a background image or color extends beyond an element’s padding or content |
background-color | Specifies the solid colors as background on an element |
background-image | Specifies one or more background images for an element |
background-origin | Specifies the origin position of a background image-across the whole element, inside the border, or inside the padding. |
background-position | Specifies the position of a background image within its container |
background-repeat | Defines if (and how) background image will repeat |
background-size | Defines the size of the background images |
border | A shorthand property that accepts multiple values for drawing a line around the element |
border-collapse | Specifies if table borders should collapse-single border/separated |
border-color | Specifies the border-color |
border-image | Shorthand property that lets you use an image as the border of an element |
border-radius | Shorthand property that lets you give any element “rounded corners” for the four border |
border-spacing | Sets how far apart the adjacent cells are between the borders |
bottom | Sets the placement of an element from the bottom of its parent element |
box-decoration-break | Lets you control how box decorations are drawn across the fragments of a “broken” element at page-break, or, for in-line elements, at line-break |
box-shadow | Used in casting shadows from elements |
box-sizing | Defines how the width and height of an element are calculated: should they include padding and borders, or not |
break-inside | Adjusts page breaks inside the current element |
caption-side | Allows you to define the position of a table caption |
caret-color | Changes the color of the cursor (caret) in inputs, textareas, or any element that is editable |
@charset | Specifies the character encoding used in the style sheet |
clear | Sets whether an element must be moved below (cleared) floating elements that precede it. It applies to float and non-floating elements |
color | Sets the color of text and text decorations |
column-count | Breaks an element’s content into the specified number of columns |
column-fill | Specifies how an element’s contents are balanced when broken into columns |
column-gap | Specifies the gap between the columns |
column-rule | Sets the width, style, and color of the line drawn between columns in a multi-column layout |
column-span | Makes it possible for an element to span across all columns |
column-width | Sets the ideal column width in a multi-column layout |
columns | Sets the column width and column count of an element |
content | Used in conjunction with the pseudo-elements:before and :after. It is used to literally insert content |
counter-increment | Increases or decreases the value of a CSS counter by a given value |
counter-reset | Create or resets a CSS counter to a given value |
cursor | Controls what the mouse cursor will look like when it is located over the element in which this property is set |
direction | Sets the direction of text, table columns, and horizontal overflow |
display | Specifies how a certain HTML element should be displayed |
empty-cells | Sets whether borders and backgrounds appear on empty cells in a table |
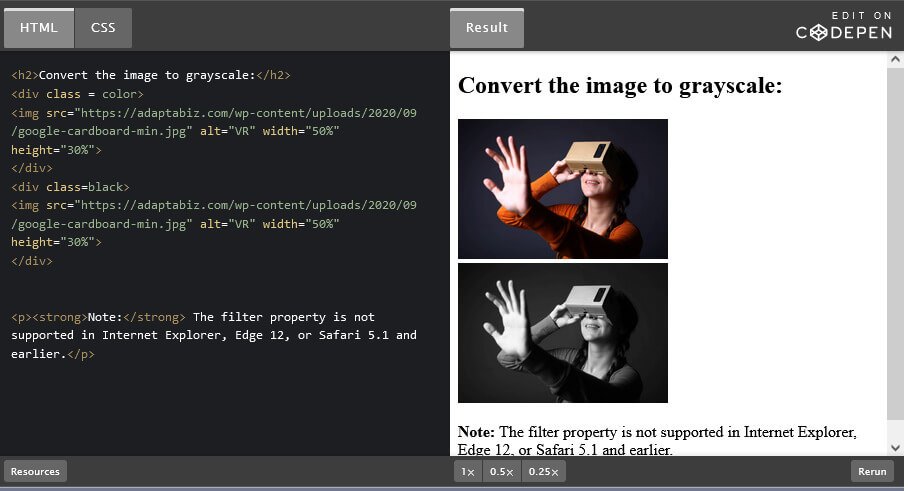
filter | Provides access to effects like blur or color shifting on an element’s rendering before the element is displayed |
flex-basis | Specifies the initial size of the flex item |
flex-direction | Specifies the direction flex items are placed in the flex container |
flex-flow | A shorthand property for the flex-direction and the flex-wrap properties |
flex-grow | Defines the ability for a flex item to grow if necessary |
flex-shrink | Determines how much the flex item will shrink relative to the rest |
flex-wrap | Sets whether flex items are forced onto one line or can wrap onto multiple lines |
float | Specifies whether or not a box should float |
font | A shorthand property for the font-style, font-variant, font-weight, font-size/line-height, and the font-family |
font-display | Defines how font files are loaded and displayed |
font-family | Defines the font that is applied to the selected element |
font-feature-settings | Controls advanced typographic features in OpenType fonts |
font-size | Specifies the size or height of the font |
font-size-adjust | Sets how the font size should be chosen based on the height of lowercase rather than capital letters |
font-stretch | Selects a normal, condensed or expanded face from a font |
font-style | Sets whether a font should be styled with a normal, italic, or oblique face from its font-family |
font-variant | Allows you to change the targeted text to small caps |
font-variant-numeric | Controls the usage of alternate glyphs for numbers, fractions, and ordinal markers |
font-weight | Sets the weight or thickness of a font |
grid-row / grid-column | Defines which row or column an element will be displayed on |
grid-template-columns | Specifies the size of the columns, and how many columns in a grid layout |
grid-template-rows | defines the line names and track sizing functions of the grid rows |
hanging-punctuation | specifies whether a punctuation mark should hang at the start or end of a line of text, it may be placed outside the line box |
height | Specifies the height of an element |
hyphens | Specifies how words should be hyphenated when text wraps across multiple lines |
image-rendering | Defines how the browser should render an image if it is scaled up or down from its original dimensions |
@import | Allows you to import a style sheet into another style sheet |
isolation | Determines whether an element must create a new stacking context |
justify-content | Defines how the browser distributes space between and around content items along the main axis of a flex container, and the inline axis of a grid container |
@keyframes | Specifies the animation code |
left | Specifies the horizontal position of a positioned element |
letter-spacing | Controls the amount of space between each letter in a given element or block of text |
line-height | Defines the amount of space above and below inline elements |
list-style | A shorthand property that sets values for three different list-related properties in one declaration |
margin | Defines the outermost portion of the box model, creating space around an element, outside of any defined borders |
max-height | Sets the maximum height of a specified element |
max-width | Sets the maximum width of a specified element |
@media | Sets the style rules for different media types/devices/sizes |
min-height | Sets the minimum height of a specified element |
min-width | Sets the minimum width of a specified element |
mix-blend-mode | Defines how an element’s content should blend with its background |
object-fit | Defines how an element responds to the height and width of its content-box |
object-position | specifies the alignment of the selected replaced element’s contents within the element’s box |
opacity | specifies how transparent an element is |
order | Sets the order to lay out an item in a flex or grid container |
orphans | Controls the minimum number of lines of a paragraph that can be left on the old page |
outline | A shorthand property to set various outline properties in a single declaration- outline-style, outline-width, and outline-color properties |
outline-offset | Offsets a defined outline from an element’s border edge by a specified amount |
overflow | Sets what to do when an element’s content is too big to fit in its block formatting context |
overflow-wrap | Applies to inline elements, setting whether the browser should insert line breaks within an otherwise unbreakable string to prevent text from overflowing its line box |
padding | Sets the padding area on all four sides of an element. It is a shorthand for padding-top, padding-right, padding-bottom, and padding-left |
page-break-after/page-break-before/page-break-inside | Properties help define how the document is supposed to behave after an element, before an element and inside and element |
perspective | Gives an element a 3D-space by affecting the distance between the Z plane and the user |
perspective-origin | determines the position at which the viewer is looking |
pointer-events | Sets under what circumstances (if any) a particular graphic element can become the target of pointer events |
position | Help you manipulate the location of an element |
quotes | Specifies which types of quotes are used when quotes are added for embedded quotations |
resize | Controls if and how an element can be resized by the user |
right | Specifies the right position of a positioned element |
scroll-behavior | Specifies whether to smoothly animate the scroll position in a scrollable box, instead of a straight jump |
tab-size | Sets the amount of spaces that display for the tab character |
table-layout | Defines what algorithm the browser should use to lay out table rows, cells, and columns |
text-align | Align the inner content of a block element |
text-align-last | Control the alignment of the last (or only) line of text right before a forced line break |
text-decoration | Sets the appearance of an underline, overline, line-through, or a combination of lines to selected text. |
text-decoration-color | Specifies the color of the text-decoration |
text-decoration-line | Specifies the type of line in a text-decoration |
text-decoration-style | Specifies the style of the line in a text decoration |
text-indent | Specifies how much horizontal space text should be moved before the beginning of the first line of the text content of an element |
text-justify | Sets what type of justification should be applied to text when text-align: justify; is set on an element |
text-overflow | Deals with situations where text is clipped when it overflows the element’s box |
text-shadow | Adds shadow to text |
text-transform | Controls text case and capitalization |
text-underline-position | sets the placement of the underline on links or on text with text-decoration property |
top | Specifies the top position of a positioned element |
transform | Allows you to visually manipulate an element by skewing, rotating, translating, or scaling |
transform-origin | Sets the origin for an element’s transformations |
transform-style | Sets whether children of an element are positioned in the 3D space or are flattened in the plane of the element |
transition | A shorthand property used to represent up to four transition-related longhand properties |
transition-delay | Defines a length of time to delay the start of a transition |
transition-duration | Sets the length of time a transition animation should take to complete |
transition-property | Sets the CSS properties to which a transition effect should be applied |
transition-timing-function | Define a function that describes how a transition will proceed over its duration, allowing a transition to change speed during its course |
unicode-bidi | Used together with the direction property, determines how bidirectional text in a document is handled |
user-select | Controls how the text in an element is allowed to be selected |
vertical-align | Controls how elements set next to each other on a line are lined up |
visibility | Specifies whether or not an element is visible |
white-space | Specifies how text is handled on the element it is applied to |
widows | Specifies the minimum number of lines of a paragraph that can fall to a new page |
width | Specifies the width of the element’s content area |
word-break | Specifies how words should break when reaching the end of a line |
word-spacing | Sets the length of space between words and between tags |
writing-mode | Sets whether lines of text are laid out horizontally or vertically, as well as the direction in which blocks progress |
z-index | Specifies the vertical stacking order of elements that overlap |
zoom | Allows you to scale your content |